|
In the previous "Starting to Plot"
section, we introduced the PlotPanel
abstract class, which we plan to use as the base class for various
graphics tasks that require scaled axes. For example, in the previous
demonstration program we created
the DemoPanel
subclass of PlotPanel
to show how to draw points with error bars. For other types of displays,
such as ploting a curved line through data points, we can create
other PlotPanel
subclasses for each case.
Here we will introduce a PlotPanel
subclass that will greatly simplify our drawing code by employing
the polymorphic techniques
discussed in Chatper 4.
DrawFunction
is an abstract class that holds a draw()
method. Subclasses of DrawFunction
override this method to create particular types of drawings such
as lines or points. The setParameters()
method in DrawFunction
allows for setting the particular attributes of the line, points,
etc. Its first argument is a 1D array and the second is a 2D array.
The subclass can use these as is convenient.
DrawPanel
receives an array of DrawFunction
objects. In DrawPanel
the paintContents()
method loops through the array and invokes the draw()
method for each
DrawFunction object. Each of the DrawFunction
objects overlays its particular drawing. This allows
for the possibility of building complex composite drawings with
great flexibility.
This approach also provides a good illustration of polymorphism,
as discussed in Chapter
4: Java. The draw()
method of the DrawFunction
base class is invoked but the method actually executed is that of
the overriding subclass. The two DrawFunction subclasses used in
the demo program below are:
- DrawLine
is a subclass of DrawFunction
that draws a straight line on the panel. The intercept and slope
of the line are passed to it via the 1D array argument in the
setParameters()
method.
- DrawPoints
is a subclass of DrawFunction
that draws a set of points and allows for optional x and y error
bars. The arrays for the coordinates and the errors are passed
via the 2D array in the second argument of the setParameters()
method.
Note that the of DrawFunction
subclass drawing settings are in the scale units (km, kg, or whatever)
of the data given to the DrawPanel.
The paintContents()
method will determine the conversion to pixel coordinates. So when
you create a particular DrawFunction
object, you only have to deal with the data's own scale units and
not worry about the display scaling.
PlotDemoApplet
below demonstrates this approach. It first creates an arbitrary
line and then some points along the line
PlotDrawApplet.java
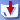 -
demonstrates DrawPanel. The DrawPanel object uses a
DrawPoints and a DrawLine object to draw a set of points
and a line through them.
-
demonstrates DrawPanel. The DrawPanel object uses a
DrawPoints and a DrawLine object to draw a set of points
and a line through them.
+ New classes:
DrawPanel.java
 -
this PlotPanel subclass invokes the draw(,,) methods
of an array of DrawFunction subclass objects. Different
types of DrawFunction subclasses
-
this PlotPanel subclass invokes the draw(,,) methods
of an array of DrawFunction subclass objects. Different
types of DrawFunction subclasses
DrawPoints.java
 -
subclass of DrawFunction for drawing points on DrawPanel.
Provides the option drawing error bars. Arrays for x
and y coordinates along with arrays for the x and y
errors are passed via a 2-D array in setParameters(,,).
-
subclass of DrawFunction for drawing points on DrawPanel.
Provides the option drawing error bars. Arrays for x
and y coordinates along with arrays for the x and y
errors are passed via a 2-D array in setParameters(,,).
DrawLine.java
 -
subclass
of DrawFunction that draws a straight line on DrawPanel.
Provides the option drawing error bars. The slope and
intercept (for y = intercept + slope*x ) are passed
via setParameters(,,).
-
subclass
of DrawFunction that draws a straight line on DrawPanel.
Provides the option drawing error bars. The slope and
intercept (for y = intercept + slope*x ) are passed
via setParameters(,,).
DrawFunction.java
 -
abstract class with a draw(,,) and a setParameters(,,)
method. The DrawPanel drawContents(,,) method loops
through an array of DrawFunction objects to invoke their
draw(,,) method and thus overlay an assortment of drawn
points, lines, etc
-
abstract class with a draw(,,) and a setParameters(,,)
method. The DrawPanel drawContents(,,) method loops
through an array of DrawFunction objects to invoke their
draw(,,) method and thus overlay an assortment of drawn
points, lines, etc
+
Previous classes:
Chapter
6:Tech: PlotPanel.java,
PlotFormat.java
|
|
Java Notes
- Illustrates polymorphic techniques with the use
of the DrawFunction
array in DrawPanel.
Though the array is of the base class type DrawFunction,
invoking its draw(,,)
method will actually invoke the overriding draw(,,)
method in the object's subclass.
|
|
/**
* Demonstrate the DrawPanel, which
invokes the draw methods
* of a list of DrawFunction objects.
This illustrates how to
* separate the display surface from
the drawings in a modular
* approach.
**/
public class PlotDrawApplet
extends JApplet
{
public void init () {
Container content_pane = getContentPane
();
// Create a line and some points
along the line
double y_data_min = 0.0;
double y_data_max = 100.0;
double x_data_min = 0.0;
double x_data_max = 500.0;
double y_intercept = 10.0;
double slope =
0.16;
double [] line_parameters = new
double[2];
line_parameters[0] = y_intercept;
line_parameters[1] = slope;
// Create the object to draw a straight
line.
DrawLine draw_line = new DrawLine
();
draw_line.setParameters (line_parameters,
null);
// Create the points data
double [] y = new double[10];
double [] x = new double[10];
double [] y_err = new double[10];
// Need a 2 D array to pass to DrawPoints
object.
double [][] data = new double[4][];
data[0] = y;
data[1] = x;
data[2] = y_err;
data[3] = null;// no error on x
coordinate
// Create some data points using
the line.
double x_pos = 45.0;
double err = 4.0;
for (int i=0; i < 10; i++){
y[i] = y_intercept
+ slope * x_pos;
x[i] = x_pos;
y_err[i]
= err;
err *= 1.20;
// let error increase with x
x_pos +=
45;
}
// Create a DrawPoints instance
to draw the points on
// the DrawPanel.
DrawPoints draw_points = new DrawPoints
();
draw_points.setParameters (null,
data);
DrawFunction [] drawFunctions
= new DrawFunction[2];
drawFunctions[0] = draw_line;
drawFunctions[1] = draw_points;
// Create an instance of DrawPanel
with the range limits and
// the functions to draw.
DrawPanel draw_panel = new DrawPanel
(y_data_min, y_data_max,
x_data_min, x_data_max,
drawFunctions);
// And add one or more panels to
the JApplet panel.
content_pane.add (draw_panel);
} // init
} // class PlotDrawApplet

|
|
import
java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* Draws a set of functions within
the plotting area.
* Instances of subclasses of DrawFunction
each draw
* their respective function on the
panel.
**/
public class DrawPanel extends PlotPanel
{
String fTitle = "Draw Functions";
String fXLabel= "Y vs X";
// Array of functions to draw.
DrawFunction [] fDrawFunctions;
// These numbers determine the axes ranges.
double fYDataMin = 0.0;
double fYDataMax = 1.0;
double fXDataMin = 0.0;
double fXDataMax = 1.0;
// Arrays to use for plotting axes scale values
double [] fXScaleValue;
double [] fYScaleValue;
// Number of values for the x and y axes scales.
int fNumYScaleValues = 2;
int fNumXScaleValues = 5;
/**
* Set the upper and lower
limits for the drawing area.
* Assumes the number
of elements in the arrays are
* the same.
**/
public DrawPanel (double y_data_min, double
y_data_max,
double
x_data_min, double x_data_max,
DrawFunction
[] draw_functions) {
fDrawFunctions = draw_functions;
fYDataMax = y_data_max;
fXDataMax = x_data_max;
fYDataMin = y_data_min;
fXDataMin = x_data_min;
getScaling ();
} // ctor
/**
* Get the values for the scaling
numbers on
* the plot axes.
**/
void getScaling () {
fYScaleValue = new double[fNumYScaleValues];
// Use lowest value of 0;
fYScaleValue[0] = fYDataMin;
fYScaleValue[fNumYScaleValues-1]
= fYDataMax;
// Then calculate the difference
between the values
double range = fYScaleValue[fNumYScaleValues-1]
-
fYScaleValue[0];
double del = range/ (fNumYScaleValues-1);
// Now set the intermediate scale
values.
for (int i=1; i < (fNumYScaleValues-1);
i++) {
fYScaleValue[i]
= i * del + fYScaleValue[0];
}
fXScaleValue = new double[fNumXScaleValues];
// First get the low and high values;
fXScaleValue[0] = fXDataMin;
fXScaleValue[fNumXScaleValues-1]
= fXDataMax;
// Then calculate the difference
between the values
range = fXScaleValue[fNumXScaleValues-1]
-
fXScaleValue[0];
del = range/ (fNumXScaleValues-1);
// Now set the intermediate scale
values.
for (int i=1; i < (fNumXScaleValues-1);
i++) {
fXScaleValue[i]
= i * del + fXScaleValue[0];
}
} // getScaling
/**
* Invoke the draw method
for the list of
* DrawFunction instances.
* Note that the frame
area is clipped so further use of
* g will also be clipped
to show only drawing within the
* scaled frame area.
**/
void paintContents (Graphics g) {
if (fDrawFunctions == null) return;
// Draw the numbers along the axes
drawAxesNumbers (g, fXScaleValue,
fYScaleValue);
// Keep drawing within the frame
box
g.setClip (fFrameX, fFrameY, fFrameWidth,
fFrameHeight);
// Now loop through all the
for (int i=0; i < fDrawFunctions.length;
i++) {
fDrawFunctions[i].draw
(
g,
fFrameX,
fFrameY,
fFrameWidth,
fFrameHeight,
fXScaleValue,fYScaleValue);
}
} // paintContents
/** Return the plot title. **/
String getTitle ()
{ return fTitle;}
/** Return the x axis label. **/
String getXLabel ()
{ return fXLabel;}
// Additional methods for setting the title
and label
/** Set plot title. **/
void setTitle (String title)
{ fTitle = title;}
/** Set x axis label. **/
void setXLabel (String x_label)
{ fXLabel = x_label;}
/** Set scaling limits for axes. **/
void setScaleLimits (double y_data_min, double
y_data_max,
double x_data_min, double x_data_max) {
this.fYDataMax = y_data_max;
this.fXDataMax = x_data_max;
this.fYDataMin = y_data_min;
this.fXDataMin = x_data_min;
getScaling ();
}
/** Pass a new array of DrawFunction
objects. **/
void setDrawFunctions (DrawFunction [] draw_functions){
fDrawFunctions = draw_functions;
}
} // class DrawPanel

|
|
/**
* Abstract base class for drawing
functions onto
* the PlotPanel subclasses.
**/
public abstract class DrawFunction
{
double [] fParameters;
double [][] fData;
Color fColor = Color.BLACK;
/**
* Abstract base class
for drawing functions onto
* the PlotPanel subclasses.
*
* @param g graphics context
* @param frameWidth display
area width in pixels.
* @param frameHeight
display area height in pixels.
* @param frameStartX
horizontal point on display where
* drawing starts in pixel
number.
* @param frameStartY
vertical point on display where
* drawing starts in pixel
number.
* @param xScale 2 dimensional
array holding lower and
* upper values of the
function input scale range.
* @param yScale 2 dimensional
array holding lower and
* upper values of the
function output scale range.
*/
public abstract void draw (Graphics g,
int frame_start_x, int frame_start_y,
int frame_width, int frame_height,
double [] x_scale, double [] y_scale);
/**
* Parameters and data for
the function.
**/
public void setParameters (double [] parameters,
double [][] data) {
fParameters = parameters;
fData = data;
}
public void setColor (Color color){
fColor = color;
}
}
// class DrawFunction

|
|
import
java.awt.*;
/** Drawing straight line onto the PlotPanel. **/
public class DrawLine extends DrawFunction
{
/**
* Draw a straight line onto
the PlotPanel.
*
* @param g graphics context
* @param frame_width
display area width in pixels.
* @param frame_height
display area height in pixels.
* @param frame_start_x
horizontal point on display where
* drawing
starts in pixel number.
* @param frame_start_y
vertical point on display where
* drawing
starts in pixel number.
* @param x_scale 2 dimensional
array holding lower and
* upper values
of the function input scale range.
* @param y_scale 2 dimensional
array holding lower and
* upper values
of the function output scale range.
**/
public void draw (Graphics g,
int frame_start_x, int frame_start_y,
int frame_width, int frame_height,
double [] x_scale, double [] y_scale) {
Color save_color = g.getColor ();
g.setColor (fColor);
// Check if ready to draw the line
if (fParameters == null) return;
// Get the number of horizontal
scale values.
int num_x_points = x_scale.length;
int num_y_points = y_scale.length;
// Get conversion factor from data
scale to frame pixels
double y_scaleFactor =
frame_height/(y_scale[num_y_points-1]
- y_scale[0]);
// Get the vertical coord vs the
first and last points on
// the horizontal axis.
double y0 = fParameters[0] + fParameters[1]
* x_scale[0];
double y1 = fParameters[0] + fParameters[1]
* x_scale[num_x_points-1];
// Convert to pixel nunber
int y_0_frame = frame_height - (int)(y0
* y_scaleFactor) +
frame_start_y;
int y_1_frame = frame_height - (int)(y1
* y_scaleFactor) +
frame_start_y;
// Don't draw outside of the frame.
g.setClip (frame_start_x, frame_start_y,
frame_width, frame_height);
// Draw the straight line.
g.drawLine (frame_start_x, y_0_frame,
frame_start_x + frame_width, y_1_frame);
g.setColor (save_color);
} // draw
} // class DrawLine

|
|
import
java.awt.*;
/**
* Drawing points on the PlotPanel.
Allow for the option
* of different symbols as well as
error bars.
**/
public class DrawPoints extends DrawFunction
{
double [] fXData;
double [] fYData;
double [] fXErr;
double [] fYErr;
// Symbol types for plotting
public final static int RECT
= 0;
public final static int RECTFILL = 1;
public final static int OVAL
= 2;
public final static int OVALFILL = 3;
int symbolType = 3;// default filled oval
Color fSymbolColor = Color.BLUE;
Color fErrorColor = Color.RED;
/**
* Draw a straight line onto
the PlotPanel.
*
* @param g graphics context
* @param frame_width
display area width in pixels.
* @param frame_height
display area height in pixels.
* @param frame_start_x
horizontal point on display where
* drawing
starts in pixel number.
* @param frame_start_y
vertical point on display where
* drawing
starts in pixel number.
* @param x_scale 2 dimensional
array holding lower and
* upper values
of the function input scale range.
* @param y_scale 2 dimensional
array holding lower and
* upper values
of the function output scale range.
**/
public void draw (Graphics g,
int
frame_start_x, int frame_start_y,
int
frame_width, int frame_height,
double
[] x_scale, double [] y_scale){
// Check if ready to draw the line
if (fXData == null || fYData ==
null) return;
Color saveColor = g.getColor ();
// Get the number of horizontal
scale values.
int num_x_points = x_scale.length;
int num_y_points = y_scale.length;
// Get conversion factor from data
scale to frame pixels
double y_scaleFactor =
frame_height/(y_scale[num_y_points-1]
- y_scale[0]);
double x_scaleFactor =
frame_width/(x_scale[num_x_points-1]
- x_scale[0]);
// Plot points
for (int i=0; i < fXData.length;
i++) {
// Convert
to pixel nunber
int y =
frame_height - (int)((fYData[i] -
y_scale[0]) * y_scaleFactor)
+
frame_start_y;
int x = (int)((fXData[i]
- x_scale[0]) * x_scaleFactor) +
frame_start_x;
// For data
symbols get size relative to the frame.
int symDim
= (int)(frame_width *.01);
// Draw
data point symbols
g.setColor
(fSymbolColor);
// Now draw
the desired symbol.
switch (
symbolType) {
case
RECT :
g.drawRect
(x-symDim,y-symDim, 2*symDim, 2*symDim);
break;
case
RECTFILL :
g.fillRect
(x-symDim,y-symDim, 2*symDim+1, 2*symDim+1);
break;
case
OVAL :
g.drawOval
(x-symDim,y-symDim, 2*symDim, 2*symDim);
break;
case
OVALFILL :
default
:
g.fillOval
(x-symDim,y-symDim, 2*symDim+1, 2*symDim+1);
break;
}
g.setColor
(fErrorColor);
// Use error
array references as flags for drawing errors
if ( fXErr
!= null) {
int
xBar = (int) (fXErr[i]*x_scaleFactor/2.0);
//
Draw x error bar
g.drawLine
(x-xBar,y,x+xBar,y);
}
if ( fYErr
!= null) {
int
yBar = (int) (fYErr[i]*y_scaleFactor/2.0);
//
Draw y error bar
g.drawLine
(x,y-yBar,x,y+yBar);
}
}
g.setColor (saveColor);
} // draw
/** Pass coords of the points to
draw. **/
public void setParameters (double [] param,
double [][] data ){
fYData = data[0];
fXData = data[1];
fYErr = data[2];
fXErr = data[3];
}
/** Set the type of symbol to use for the points.
**/
public void setSymbolType (int type){
symbolType = type;
}
} // class DrawPoints

|
References & Web Resources
Last Update: Oct. 30, 2004
|
