|
|
The SimServer
program provides each client a dedicated simulator of the mass
drop experiment discussed in Chapter
9: Physics. The server connects to the clients via a socket.
The main program hands off the client socket to an instance of
SimWorker
whose job is to tend to the needs of the client.
The text area in the main program displays messages that indicate
the status of the connections to the clients and of the simulations.
A text field allows for choosing a different port for the socket
connections.
The SimWorker
creates an instance of SimApplet,
which derives from the mass drop simulator code in the Chapter
9: Physics demonstration. (The SimClient
holds the analysis part of that demo.) The SimWorker
then acts as an intermediary between the SimApplet
and the SimClient.
The SimWorker
implements the SimController
interface, which includes the method
message(int
flag, int iData, double [][] fp).
The SimApplet
instance uses this method to pass instructions and data to the
SimWorker
(and thus on to the SimClient.)
An interface allows for the possibility that other simulators
could be used with SimWorker
or, conversely, that other types of workers that implement the
interface could be used without modifying the simulator code.
|
The SimServer Application
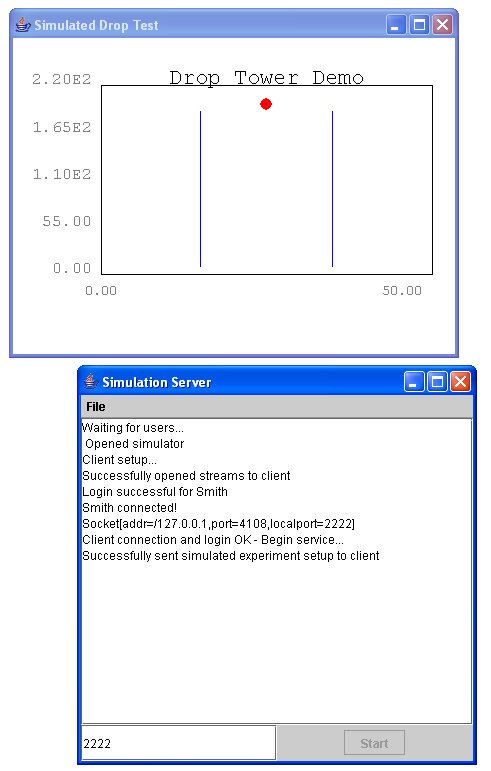
SimServer.java
-
This application monitors a ServerSocket for requests
for connections from clients. The port can be selected
in the text field (default 2222). The text area shows
messages indicating the status of the connection with
the client(s). When
a connection socket is created, it is handed over to
a SimWorker object that is dedicated to serving that
client. Maintains a list of clients and limits the total
to a set number.
New
classes:
SimWorker.java
- created by the SimServer to tend to the socket connection
to the client. It also creates an instance of SimApplet
to carry out the simulation. When the client sends an
instruction to start the run, the instruction goes through
the SimWorker object. Similarly, the data from the simulation
goes through the SimWorker to the client. Various setup
parameters are also passed back and forth between the
simulator and the client via the SimWorker.
SimApplet.java
-
simulate the dropping of a mass and the measurement
of its position every DT time interval. Derived from
Ch.
9: Physics: DropTestAnalysisApplet.java.
SimController.java
- interface implemented by SimWorker. Provides a generic
message() method for the SimApplet object to callback
to the SimWorker object that created it. Could allow
for using the SimWorker with other types of simulators.
NetStreamMethods.java
- convenient utility class with methods for reading
and writing over the socket streams.
SimUtil.java
- another convenience class that holds some constants
used in the communications protocols.
+ Previous classes:
Ch.9:
Physics:
DropPanelDetect.java,
DropModelDetect.java,
DropDetector2.java,
Detector.java
Ch.6:
Tech: PlotPanel.java,
PlotFormat.java
|
//package
SimClientServer;
// Begun from StartJApp5
import java.net.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
/**
* Server for a Prototype Remote Data
Monitoring System
*
* SimServer provides simulated data to multiple
instances of SimClient.
* A SimClient connects via a socket and executes
a simple login procedure.
*
* An instance of the thread class SimWorker
is assigned to each
* client socket. Via the socket, the client sends
setup information for
* the simulation, initiates a "run" of the sim, and
data from each
* drop is sent to the client.The SimWorker includes
methods to read
* and write strings and numerical data with streams
to the client.
*
* Multiple clients can connect simultaneously.
The default max users value
* is set to 10.
*
**/
public class SimServer extends JFrame
implements ActionListener,
Runnable
{
// GUI setup attributes
JMenuItem fMenuClose;
JTextArea fTextArea;
JTextField fTextField;
JButton fStartButton;
// Networking setup
// Use a Vector to keep track of the DataWorker
list.
Vector fWorkerList;
// Connect to clients
ServerSocket fServerSocket;
int fDataServerPort = 2222;// Default port number
// Client counting and limit
static int fClientCounter__ = 0;
static int fMaxClients__ = 10;
// Number of data values per set or "event"
static int fNumDataVals__ = 6;
// Flag for the server socket loop.
boolean fKeepServing = true;
/**
* Open frame for the user interface.
*/
public static void main (String [] args) {
// Can pass frame title
in command line arguments
String title = "Simulation Server";
if (args.length != 0) title = args[0];
SimServer f = new SimServer (title);
f.setVisible (true);
} // main
/**
* Pass a title to the frame via
the constructor
* argument. Build the GUI.
*/
SimServer (String title) {
super (title);
// Create the vector to list the
DataWorker objects
fWorkerList = new Vector
();
// Create a user interface.
setLayout (new BorderLayout ());
fTextArea = new JTextArea ("");
JScrollPane area_scroll_pane = new
JScrollPane (fTextArea);
add (area_scroll_pane, "Center");
// Create a panel with a textfield
and two buttons
fTextField = new JTextField ("2222");
fStartButton = new JButton ("Start");
fStartButton.addActionListener (this);
JPanel panel = new JPanel (new GridLayout
(1,2));
JPanel button_panel = new JPanel
();
panel.add (fTextField);
button_panel.add (fStartButton);
panel.add (button_panel);
add (panel, "South");
// Use the helper method makeMenuItem
// for making the menu items and
registering
// their listener.
JMenu m = new JMenu ("File");
// Use File menu to hold Quit command.
m.add (fMenuClose = makeMenuItem
("Quit"));
JMenuBar mb = new JMenuBar ();
mb.add (m);
setJMenuBar (mb);
setSize (400,400);
setDefaultCloseOperation (JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
} // ctor
/**
* Process events from the frame
menu and the chooser.
**/
public void actionPerformed (ActionEvent e)
{
boolean status = false;
String command = e.getActionCommand
();
if ( command.equals ("Start") )
{
try{
fDataServerPort
= Integer.parseInt (fTextField.getText ());
}
catch (NumberFormatException
nfe){
println
("Bad port number");
return;
}
fStartButton.setEnabled
(false);
Thread thread
= new Thread (this);
thread.start
();
} else if (command.equals ("Quit")
){
fKeepServing
= false;
for (Enumeration
en = fWorkerList.elements () ;
en.hasMoreElements
();)
((SimWorker)
(en.nextElement ())).signOff ();
dispose
();
}
} // actionPerformed
/**
* Create a ServerSocket
and loop waiting for clients.
**/
public void run () {
// The server_socket is used to
make connections to
// DataClients at this port number
try {
fServerSocket = new
ServerSocket (fDataServerPort);
}
catch (IOException e) {
println
("Error in server socket");
return;
}
println ("Waiting for users...");
// Loop here to grab clients
while (fKeepServing) {
try {
// accept
() blocks until a connection is made
Socket socket
= fServerSocket.accept ();
// Do the
setup this socket and then loop
// back
around to wait for the next DataClient.
SimWorker
worker = new SimWorker (this, socket);
Thread thread
= new Thread (worker);
thread.start
();
}
catch (IOException ioe)
{
println
("IOException: <" + ioe + ">");
break;
}
catch (Exception e)
{
println
("Exception: <" + e + ">");
break;
}
}
} // run
/**
* A DataWorker will set up the connection
with the client. If it
* decides that the conditions are
OK, then it will invoke this
* method so that the parent server
will add the worker to its list.
*
* We synchronize the method to avoid
any problems with multiple
* clients interfering with each
other.
**/
public synchronized void clientConnected (SimWorker
worker) {
fWorkerList.add (worker);
fClientCounter__++;
}
/**
* When a client disconnects, the
DataWorker object will
* call back to this method to remove
itself from the list
* of workers.
*
* We synchronize the method to avoid
any problems with multiple
* clients interfering with each
other.
**/
public synchronized void clientDisconnected
(String user,
SimWorker worker) {
println ("Client: "+user+" disconnected");
fWorkerList.remove (worker);
fClientCounter__--;
} // clientDisconnected
/**
* When a DataWorker makes the connection,
it checks to see if there
* is room on the server for it.
*
* We synchronize the method to avoid
any problems with multiple
* clients interfering with each
other.
**/
public synchronized boolean clientPermit ()
{
if ( fWorkerList.size () < fMaxClients__)
return true;
else
return false;
} // clientPermit
/**
* This "helper method" makes a menu
item and then
* registers this object as a listener
to it.
**/
private JMenuItem makeMenuItem (String name)
{
JMenuItem m = new JMenuItem ( name
);
m.addActionListener ( this );
return m;
} // makeMenuItem
/**
* Utility method to send
messages to the
* text area.
**/
public void println (String str) {
fTextArea.append (str +"\n");
repaint ();
} // println
} // class SimServer |
package
SimClientServer;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
/**
* SimServer creates instances of this class
to service
* SimClient connections. It creates a SimApplet
mas drop
* experiment simulator. Once the connection
is set up using the Socket
* instance passed to it from the main server
program, the client can
* initiate and run the simulation via the methods
in this class.
*
* For convenience (avoiding lots
of try-catch coding, this class extends
* the NetStreamMethods class and uses its methods
to read and write with
* the client.
*
* A SimWorker object runs via its own thread.
To remain alive while waiting
* for instructions from the client, a synchronized
method executes the
* wait () method. The callback (see
the message () method) from the
* simulator will cause notifyAll () to release
the thread from its wait
* state.
*
* Each client deals with its own SimApplet simulation.
The SimApplet
* sends instructions and data back to its corresponding
SimWorker via
* the message () method of the SimController
interface. The message ()
* method also sends data on to the client.
**/
public class SimWorker extends NetStreamMethods
implements Runnable, SimController {
// The parent server.
SimServer fServer;
// Simulation variables
SimApplet fSimApplet;
JFrame fFrame; // Frame to hold the simulation
applet
// Name of the client
String fUser;
// Connection to the client passed from the
main control progam.
Socket fSocket;
// Utility buffer arrayfServer.
int [] fIBuffer;
double [] fDBuffer;
// Flag for the primary loop in the run () method.
boolean fKeepRunning = true;
/**
* Pass reference to the
owner DataServer_JApp5 and the
* index number for this
DataSender instance.
*
* Create an instance
of SimApplet and display in its own frame.
**/
public SimWorker (SimServer s, Socket socket)
{
fServer = s;
fSocket = socket;
// Create the simulation applet
and open in a separate frame.
fSimApplet = new SimApplet ();
fSimApplet.fInBrowser = false;
fSimApplet.init ();
// Tell the SimApplet to communicate
with this controller
fSimApplet.setController (this);
// Following anonymous class used
to close window & exit program
fFrame = new JFrame ("Simulated
Drop Test");
fFrame.addWindowListener
( new WindowAdapter ()
{
public void
windowClosing (WindowEvent e) {
fFrame.dispose ();
}
}
);
// Add applet to the frame
fFrame.getContentPane ().add ( fSimApplet);
fFrame.setSize (new Dimension (450,350));
fFrame.setVisible (true);
fServer.println (" Opened simulator");
} // ctor
/**
* The communications
with the client take place in this
* run () method. It begins
by setting up the socket communications
* and carrying out a
login procedure. Then the parameters of the
* simulated experiment
are sent to the client for its display and
* analysis purposefServer.
**/
public void run () {
// Do all the stream setup with
the client and carry out
// the login procedure.
if (!serviceSetup ()){
signOff
();
return;
}
fServer.println ("Client connection
and login OK - Begin service...");
// Send to the client the setup
parameters for the simulated experiment
if (!sendExptSetup ()){
signOff
();
return;
}
fServer.println ("Successfully sent
simulated experiment setup to client");
// Now begin the loop for communicating
with the client.
while (fKeepRunning){
// Wait for a request
from the DataClient
int clientRequest =
readNetInputInt ();
if (fFailedIO) break;
int nval = 0;
// Use a switch statement
to select the operation
switch (clientRequest)
{
case SimUtil.START://
Start a run.
//
print message
fServer.println
(" Client "+fUser+ " starts simulation");
//
Begin by obtaining the run setup (e.g. number
of
//
events to simulate) from the client.
//
First the size of the integer array
nval
= readNetInputInt ();
if
(fFailedIO) break;
//
Read the integer array
fIBuffer
= readNetInputIntArray (fIBuffer, nval);
if
(fFailedIO ) break;
//
Then the size of the floating point array
nval
= readNetInputInt ();
if
(fFailedIO) break;
//
Read the double array.
fDBuffer
= readNetInputDoubleArray (fDBuffer, nval);
if
(fFailedIO ) break;
//
Now send the run setup arrays to the SimApple simulation.
//
The method returns after STARTING THE RUN of the simulator.
fSimApplet.externalControl
(SimUtil.START, fIBuffer, fDBuffer);
//
The run has started so this thread needs to wait until
//
all the data is sent from the simulation via the message
method.
//
The run cannot be stopped once it startfServer.
waitForData
();
break;
case SimUtil.STOP:
// End simulation program.
//
print message
fServer.println
(" Client "+fUser+ " stops simulation");
fFrame.dispose
();
fSimApplet
= null;
fKeepRunning
= false;
break;
}
// A failed read or
write ends program.
if ( fFailedIO) break;
}
// Send message back to the text
area in the frame.
fServer.println (fUser + " has disconnected.");
// Do any other tasks for ending
the worker.
signOff ();
} // run
/**
* Wait here for the SimApplet
object to send the drop event data
* via the message ()
method. When finished, that method will
* invoke notifyAll (),
whick will release this thread to continue.
**/
synchronized void waitForData (){
// Remain here until notifyAll invoked
in message () method.
try{
wait ();
}
catch (Exception e)
{}
} // waitForData
/**
* SimApplet object "calls
back" with this method. It can
* send its data for each
event (drop) and it can indicate
* the end of the run
and then release the lock
* in waitForData ().
* SimData puts two 1-d
arrays for the time and position
* measurements into a
2-D array.
**/
public synchronized void message (int cmd, int
nval,
double [][] data){
// Tell the client what is coming
writeNetOutputInt (cmd);
if ( fFailedIO) return;
// Then do one of the following
switch (cmd) {
case SimUtil.EVENT_DATA:
// Send client the drop measurements
// Tell
client how many values coming
writeNetOutputInt
(nval);
if ( fFailedIO)
break;
// Send
the time array.
writeNetOutputDoubleArray
(data[0], nval);
if ( fFailedIO)
break;
// Send
the position array
writeNetOutputDoubleArray
(data[1], nval);
break;
case SimUtil.RUN_DONE:
// Run done, release
notifyAll
();
fServer.println
("Run done");
break;
}
} // message
/**
* Set up the connection to the client.
This requires obtaining the
* IO streams, carrying out the login
prototcol, and then starting
* a DataWorker thread to tend to
the client.
*
* The bookkeeping code is a bit
messy because we check both reads
* and writes for errors in case
the connection breaks down.
*
* The reads catch their own IOExceptions
and return a null, while
* string writes use a PrintWriter
that doesn't throw IOException. So
* we use the checkError () method
and throw it ourselvefServer.
**/
public boolean serviceSetup () {
fServer.println ("Client setup...");
// First get the in/out streams
from the socket to the client
try {
fNetInputStream =
fSocket.getInputStream ();
}
catch (IOException ioe){
fServer.println ("Unable
to open input stream");
return false;
}
try {
fNetOutputStream = fSocket.getOutputStream
();
} catch (IOException ioe){
fServer.println ("Unable
to open output streams");
return false;
}
fServer.println ("Successfully opened
streams to client");
// Create a PrintWriter class for
sending text to the client.
// The writeNetOutputLine method
will use this clasfServer.
try{
fPrintWriter = new PrintWriter
(
new OutputStreamWriter
(fNetOutputStream, "8859_1"), true );
}
catch (IOException ioe){
fServer.println ("Fails
to open PrintWriter to client!");
return false;
}
// Check if the server has room
for this client.
// If not, then send a message to
this client to tell it the bad news.
if (!fServer.clientPermit () ) {
String msg=
"Sorry, We've reached maximum of clients";
writeNetOutputLine
(msg);
if (fFailedIO)
{
fServer.println
("Connection fails during login");
return
false;
}
fServer.println
(msg);
return false;
}
// Get a DataInputStream wrapper
so we can use its readLine () methods.
fNetInputReader =
new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader
(fNetInputStream));
// Do a simple login protocol. Send
a request for the users name.
// Note a password check could be
added here.
writeNetOutputLine ( "Username:
");
if (fFailedIO) {
fServer.println ("Connection
fails during login");
return false;
}
// Read the user name.
fUser = readNetInputLine ();
if (fUser == null ) {
fServer.println
("Connection fails during login");
return false;
}
// Send a message that the login
is OK.
writeNetOutputLine ("Login successful");
if (fFailedIO) {
fServer.println
("Connection fails during login for " + fUser);
return false;
}
fServer.println ("Login successful
for " + fUser);
fServer.println (fUser + " connected!
");
fServer.println (fSocket.toString
());
// The login is successful so now
create a DataWorker to
// service this client. Pass it
an ID number
fServer.clientConnected (this);
// Get a data output stream for
writing numerical data to the client
fNetDataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream
(fNetOutputStream);
// Get a data input stream for reading
numerical data from the client
fNetDataInputStream = new DataInputStream
(fNetInputStream);
return true;
} // serviceSetup
/**
* Get the parameters
for the experiment that SimApplet will simulate
* and send to the client.
**/
boolean sendExptSetup () {
// Get the four setup parameters
from the SimApplet
fDBuffer = new double[4];
fSimApplet.externalControl ( SimUtil.GET_SETUP,
null, fDBuffer);
// Tell client the expt setup is
coming
writeNetOutputInt (SimUtil.INIT);
if (fFailedIO) {
fServer.println
("Failed sending setup message to client");
return false;
}
// Send array size.
writeNetOutputInt (fDBuffer.length);
if (fFailedIO) {
fServer.println
("Failed sending setup array size to client");
return false;
}
// Send the setup array
writeNetOutputDoubleArray (fDBuffer,
fDBuffer.length);
if (fFailedIO) {
fServer.println
("Failed sending setup array to client");
return false;
}
// Setup sent successfully.
return true;
} // sendExptSetup
/** Whenever this client disconnects tell the
parent.**/
public void signOff () {
try {
fSocket.close ();
}
catch (Exception e){
fServer.println ("Socket
close exception for " + fUser);
}
// Tell server to remove this worker
from its list
fServer.clientDisconnected (fUser,this);
// Shut down the applet
fFrame.setVisible (false);
fFrame.dispose ();
fSimApplet = null;
fServer.println ("Close sim & socket");
} // signOff
} // class SimWorker |
package
SimClientServer;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
/**
* This program simulates an experiment in which
measurements
* are made during the fall of a mass in a constant
gravitational
* field that will be used to determine the acceleration
constant.
* It illustrates the basic components involved
with a simulation
* of any physics experiment.
*
* The applet uses DropPanelDetect to simulate
the dropping of a
* mass in a constant gravitational field. The
* DropDetector class draws the detector.
*
*
* Data for each drop is passed to an instance
of DropAnalyzer,
* which saves the data. At the end of the run (a
set of drops),
* the analyzer plots Yaverage vs. Time and fits
the points to
* a polynominal c + bT + cT^2. From the c coefficient
the gravitational
* value can be determined.
*
* The java.util.Timer and java.util.TimerTask
are used
* to update the animation of the drop.
*
**/
public class SimApplet extends JApplet
{
// Another class can control this applet simulation
if it
// implements the SimController interface.
SimController fSimController;
// 2-D array used to pass data to the controller.
double fData[][] = new double [2][];
// The DropPanel displays the animation of the
// falling mass.
DropPanelDetect fDropPanel;
// The DropModel generates the physics data.
DropModelDetect fDropModel;
// Use a detector to measure the drop times.
Detector fDetector;
// Use the HistPanel JPanel subclass here
HistPanel fHistPanel;
Histogram fHistogram;
int fNumDataPoints = 100;
boolean fMakingHist = false;
boolean fUpdateDisplay = false;
// Use the java.util Timer and TimerTask combo
// for timing events.
java.util.Timer fTimer;
// A text field for getting number of drops
per
// run and the position smearing std.dev. in
cm.
JTextField fMaxNumDropsField ;
JTextField fPosSigmaFactorField;
// Flag for whether the applet is in a browser
// or running via the main () below.
boolean fInBrowser = true;
//Buttons
JButton fGoButton; // start drop
JButton fClearButton;// resets histogram
JButton fExitButton;
// Starting coordinates of drop
double fXBallStart = 25.0; // cm
double fYBallStart = 200.0; // cm
double fYBallEnd = 0.0;
// cm
// Range of the drop time.
double fTStart = 0.00; // sec
double fTEnd = 0.75; // sec
// SD in the measured values for the marker
positions and t (sec).
// (Allow for smearing of marker
position for further experimentation.)
double [] fMeasurementSigmas = {2.0, 0.0};
// Integer and double arrays to pass info to
the detector
int [] fDetectorSetup;
double [] fDetectorParameters;
// Coordinate of ball.
double fXBall;
double fYBall;
// Initial velocity.
double fVfYBallStart = 0.0;
double fVfXBallStart = 0.0;
// Time in millisecs for the drop
double fTDropTotal;
double fTFrame = 0.020; // in secs
// Speed up or slow down factor for animation:
double fTFactor = 1.0;
// Allow for multiple drops per "run"
int fMaxNumDrops = 10;
int fNumDrops = 0;
// Number of times to measure the position during
the drop.
int fMaxNumMeasurements = 40;
/**
* Initialize the display.
Create Detector and Model
* objects to use for
the physics and experiment simulation.
* DropPanelDetect displays
the dropping ball and the
* detector. Add a HistPanel
to display the data.
**/
public void init () {
// Create a detector
fDetector = new DropDetector2 ();
// Need arrays to pass setup info
to the detector.
fDetectorSetup = new int[1];
fDetectorSetup[0] = fMaxNumMeasurements;
// Do a measurement for every frame
fDetectorParameters = new double[1];
fDetectorParameters[0] = fTFrame;
// Pass the detector the necesary
setup info
fDetector.init (fDetectorSetup,
fDetectorParameters, fMeasurementSigmas);
// Create the drop physics model
fDropModel = new DropModelDetect
(fDetector);
fDropModel.reset (fYBallStart, fVfYBallStart);
// Create a User Interface with
a textarea with sroll bars
// and a Go button to initiate processing
and a Clear button
// to clear the textarea.
JPanel panel = new JPanel (new BorderLayout
());
// Create an instance of the DropPanel
// Make the panel 10% taller than
starting position.
fDropPanel = new DropPanelDetect
(fYBallStart * 1.1, 0.0, fDetector);
panel.add (fDropPanel,"Center");
// Add text area with scrolling
to the contentPane.
add (panel);
} // init
/** Stop the run. **/
public void stop () {
runDone ();
}
/** In the constructor pass the reference to
the SimController
* to opperate this simulation.
**/
public void setController (SimController simController)
{
fSimController = simController;
}
/**
* This method allows an external
class, such as the SimServer,
* to control the drop simulation.
Pass the parameters needed for
* the simulation via the array arguments.
**/
public void externalControl (int control, int
[] valInt,
double [] valFP) {
switch (control) {
case SimUtil.START:
//
Get the number of drops & max measures per drop.
fMaxNumDrops
= valInt[0];
fDetectorSetup[0]
= valInt[1]; //= fMaxNumMeasurements
//
and the smearing on the position measurements
fMeasurementSigmas[0]
= valFP[0]; // = std. dev. on y
//
and the fTFrame
fDetectorParameters[0]
= valFP[1];// = fTFrame
//
Update the position smearing
fDetector.init
(fDetectorSetup, fDetectorParameters,
fMeasurementSigmas);
//
Reset everything and start the run again.
dropReset
();
break;
case SimUtil.GET_SETUP:
//
Use the FP data buffer to send the init data to the
//
simulation controller.
valFP[0]
= fYBallEnd;
valFP[1]
= fYBallStart;
valFP[2]
= fTStart;
valFP[3]
= fTEnd;
break;
case SimUtil.STOP:
runDone
();
break;
}
} // externalControl
/**
* Use the inner class technique
to define the
* TimerTask subclass for stepping
through the
* drop calculation and the frame
refresh.
* Use the real time in the drop
calculation instead
* of the given frame rate times
in case there were
* delays from thread interruptions,
the processing
* in the parts of the program take
extra time, etc.
**/
class PaintHistTask extends java.util.TimerTask
{
public void run () {
// Drop the ball
fYBall = fDropModel.step
(fTFactor * fTFrame);
// Update the position
of the ball in the
// animation and redraw
the frame.
fDropPanel.updatePosition
(fXBall, fYBall);
// Check if ball has
crossed the finish line.
if (fYBall <= fYBallEnd)
dropDone ();
} // run
} // class PaintHistTask
/**
* Before each set of
drops, need to create a new timer,
* and set up its schedule.
The PaintHistTask innner class
* object will do the
setup for each frame of a drop animation.
**/
void dropReset () {
// Before starting the drop, create
the timer task
// that will cause the histogram
display to update
// during the filling.
// Create a timer. TimerTask created
in MakeHist ()
fTimer = new java.util.Timer ();
fDropModel.reset (fYBallStart, fVfYBallStart);
fDropPanel.reset (fXBallStart, fYBallStart);
// Reset time sum
fTDropTotal = 0.0;
fNumDrops = 0;
fYBall = fYBallStart;
fXBall = fXBallStart;
// Reset the detector.
fDetector.reset ();
repaint ();
// Start the timer after 20ms and
then repeat calls
// to run in PaintHistTask object
by the rate set by
// the fTFrame value.
fTimer.schedule (new PaintHistTask
(), 20, (int) (fTFrame*1000));
} // dropReset
/**
* Invoked after a drop
ends bottom. Reset
* all the parameters
to set up for another drop.
**/
public void dropDone () {
// Get the data (times
and positions during the drop)
// from the detector and analyze
it
fData = fDetector.getResults ();
int num_measures = fDetector.getNumMeasurements
();
// Send the event data to the controller
// Two arrays (times
and positions) must be sent.
fSimController.message (SimUtil.EVENT_DATA,
num_measures, fData);
++fNumDrops;
// Check if all drops completed.
if (fNumDrops == fMaxNumDrops){
// If so
then finish up the data recording
// for this
run and return.
runDone
();
return;
}
// Reset time sum
fTDropTotal = 0.0;
fYBall = fYBallStart;
fXBall = fXBallStart;
fDropPanel.reset (fXBallStart, fYBallStart);
fDropModel.reset (fYBallStart, fVfYBallStart);
fDetector.reset ();
} // dropDone
/**
* Invoked when all the
drops in a run (set of drops) are done.
* Kills the timer to
stop the animation. (A new timer will be
* created in the dropReset
() for the next run.)
* Tell the DropAnalyser
instance to do its job on the run data.
**/
public void runDone () {
// Stop the animation.
fTimer.cancel ();
// Tell controller that run is done.
fSimController.message (SimUtil.RUN_DONE,
-1, null);
} // runDone
} // class SimApplet |
package
SimClientServer;
public interface SimController {
public void message (int flag, int iData,
double [][] fp);
} // SimController |
package
SimClientServer;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
import java.util.*;
/**
* This utility class provides methods for streamed
I/O
* that catch the IO exceptions and set a flag
to indicate
* an IO error. This can be convenient when a
program needs
* many read/write operations and the try/catch
bracketing
* makes the code messy and difficult to read.
*
* The class also provides methods for reading
a set of data
* into an array. Similarily, there are methods
for writing
* arrays into the stream.
**/
public class NetStreamMethods {
// I/O streams
InputStream fNetInputStream;
OutputStream fNetOutputStream;
// Wrapped I/O streams
BufferedReader fNetInputReader;
DataInputStream fNetDataInputStream;
DataOutputStream fNetDataOutputStream;
PrintWriter fPrintWriter;
boolean fFailedIO = false; // Flag
/**
* Utility method to read a string
line from a
* BufferedReader stream
**/
String readNetInputLine () {
try {
return fNetInputReader.readLine
();
}
catch (IOException e) {
fFailedIO = true;
return null;
}
} // readNetInputLine
/**
* Utility method to read
an integer value
* from a DataInputStream
**/
int readNetInputInt () {
// Read one value at a time and
fill array.
try {
return fNetDataInputStream.readInt
();
}
catch (IOException ioe) {
fFailedIO = true;
return -1;
}
} // readNetInputInt
/**
* Utility method to read a double
value from
* a DataInputStream.
**/
double readNetInputDouble () {
// Read one value at a time and
fill array.
try {
return fNetDataInputStream.readDouble
();
}
catch (IOException ioe) {
fFailedIO = true;
return -1.0;
}
} // readNetInputDouble
/**
* Utility method to read an integer
array from
* a DataInputStream.
**/
int [] readNetInputIntArray (int [] buffer,
int numElements) {
if ( buffer == null || buffer.length
< numElements)
buffer =
new int[numElements];
// Read one value at a time and
fill array.
for (int i=0; i < numElements; i++)
{
try {
buffer[i]
= fNetDataInputStream.readInt ();
}
catch (IOException
ioe){
fFailedIO = true;
return null;
}
}
return buffer;
} // readNetInputIntArray
/**
* Utility method to
read a double array from a DataInputStream
**/
double [] readNetInputDoubleArray (double []
buffer,
int numElements) {
if (buffer == null || buffer.length
< numElements)
buffer =
new double[numElements];
// Read one value at a time and
fill array.
for (int i=0; i< numElements; i++){
try{
buffer[i]
= fNetDataInputStream.readDouble ();
}
catch (IOException
ioe){
fFailedIO = true;
return null;
}
}
return buffer;
} // readNetInputDoubleArray
/**
* Output is wrapped with a PrintWriter,
which doesn't throw
* IOException. So we use the checkError
() method and set the
* flag for failed output.
**/
void writeNetOutputLine (String string) {
fPrintWriter.println (string);
if (fPrintWriter.checkError ())
{
fFailedIO
= true;
return;
}
fPrintWriter.flush ();
if (fPrintWriter.checkError ())
{
fFailedIO
= true;
return;
}
} // writeNetOutputLine
/**
* Utility method to write integer
values to the output stream.
* If an IOException occurs, set
flag and return;
**/
void writeNetOutputInt (int i) {
try {
fNetDataOutputStream.writeInt
(i);
fNetDataOutputStream.flush
();
}
catch (IOException ioe){
fFailedIO = true;
return;
}
} // writeNetOutputInt
/**
* Utility method to write float
values to the output stream.
* If an IOException occurs, set
flag and return;
**/
void writeNetOutputFloat (float f) {
try {
fNetDataOutputStream.writeFloat
(f);
fNetDataOutputStream.flush
();
}
catch (IOException ioe){
fFailedIO = true;
return;
}
} // writeNetOutputFloat
/**
* Utility method to write float
values to the output stream.
* If an IOException occurs, set
flag and return;
**/
void writeNetOutputDouble (double d) {
try {
fNetDataOutputStream.writeDouble
(d);
fNetDataOutputStream.flush
();
}
catch (IOException ioe) {
fFailedIO = true;
return;
}
} // writeNetOutputDouble
/**
* Utility method to write an array
of int values to
* the output stream.
* If an IOException occurs, set
flag and return;
**/
void writeNetOutputIntArray (int [] iArray,
int
numElements){
// Loop through array and write
element
// each to the stream.
for (int i=0; i < numElements; i++)
{
// Pass
only integer values;
writeNetOutputInt
(iArray[i]);
if (fFailedIO)
return;
}
} // writeNetOutputIntArray
/**
* Utility method to write an array
of int values to
* the output stream.
* If an IOException occurs, set
flag and return;
**/
void writeNetOutputDoubleArray (double [] dArray,
int
numElements) {
// Loop through array and write
element
// each to the stream.
for (int i=0; i < numElements; i++){
// Pass
only integer values;
writeNetOutputDouble
(dArray[i]);
if (fFailedIO)
return;
}
} // writeNetOutputDoubleArray
} // class NetStreamMethods |
package
SimClientServer;
/**
* This class is just for holding
constants needed for
* communications between the server
and client.
**/
public class SimUtil {
public static final int INIT =
1;
public static final int START
= 2;
public static final int STOP =
3;
public static final int RUN_DONE =
4;
public static final int EVENT_DATA =
5;
public static final int GET_SETUP
= 6;
} // class SimUtil |
Most recent update: Oct. 25, 2005
|
|
|

