|
|
The DataClient
program, discussed in detail on the previous
page, can run either as an applet or a application. Below
it is shown as an applet. The complete code listings of DataClient
and DataClientWorker
classes are also provided.
Note: This applet generates a
security exception when it attempts to open a socket to the
DataServer unless the server is
running on the same machine as the applet. (Also, the host address
would need to be changed to the address of the host from which
the applet was downloaded.)
For your own experimentation, you should download the files
for both the client and server to your machine. Then compile
and run them there. (You can use the host address 127.0.0.1
that points to the local machine.)
DataClient
Applet
|
|
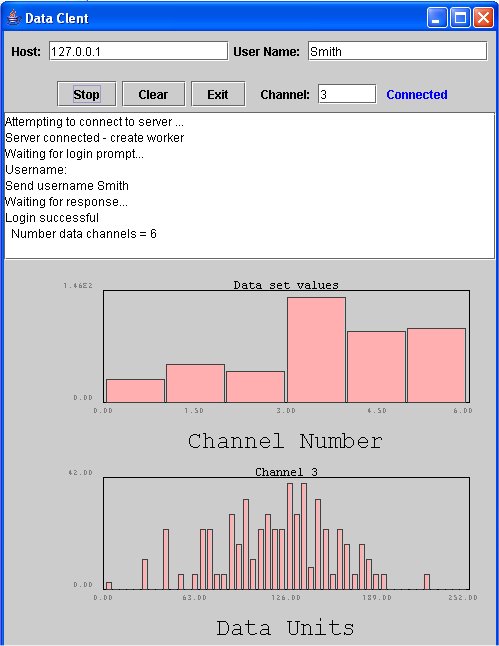
Image of DataClient
in action
DataClient.java
-
Create an interface for the user to initiate a connection
with the server at the given host address. It communicates
via a socket at port 2222. The user name is required
for the login. A text area displays messages generated
for different steps in the setup and communications
with the server.
The
server sends a set of data for each request. The top
histogram shows the values in each data channel in each
set of data. The lower histogram displays a distribution
of values for one channel over many sets of data.
+
Helper class:
DataClientWorker.java
- this Thread subclass communicates with the server
and periodically requests a set of data. When it receives
the data it passes it to the DataClient_JApplet11 parent,
which then displays the data in the histograms.
+
Previous classes:
Ch.8:Tech:
HistogramStatR1.java,
HistogramAdaptR1.java
Ch.6:Tech:
Histogram.java,
HistPanel.java
Ch.6:Tech:
PlotPanel.java,
PlotFormat.java
|
|
package
DataMonitor;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
/**
*
* A Prototype Remote Data Monitoring
System
*
* DataClientdisplays data sent
by DataServer. At a given time
* interval, DataClient requests
a set of data from the server.
* The server sends first an integer
for the number of data points
* to be sent and then sends that
many integer values.
*
* DataClient runs both as a standalone
app or in a browser web page.
*
* The User Interface displays several
items of interest:
* - The host IP and username are
displayed in TextFields
* - Stop/Stop button can interrupt
and restart the connection.
* - A label displays the status
of the connection
* - a TextArea displays the current
data.
* - One histogram displays the
values in each channel of a data set.
* - The second histogram displays
the distribution of values for one
* channel of data.
The number for the desired channel is entered
* into a text field.
*
* The thread class fDataClientWorker
is used to send requests for
* data and to read the data. The
fDataClientWorker consists primarily
* of a run () method. It calls
back to the setData (int []) method
* to send the data set obtained
fromthe server.
**/
public class DataClient extends JApplet
implements ActionListener
{
// GUI setup
// First histogram will show the data values
in each set
// obtained from the server.
HistPanel fHistDataPanel = null;
Histogram fHistData = null;
// Second histogram plots the values of one
channel in the
// data set.
HistPanel fHistChanPanel = null;
// Histogram of a data channel
HistogramAdaptR1 fHistChan = null;
// Initial array size in HistogramAdaptR1
to hold values.
int fHistArraySize = 1000;
// UI components
JLabel fStatusLabel =
null;
JTextField fHostField =
null;
JTextField fUserNameField =
null;
JTextField fChanField =
null;
JTextArea fMessageArea =
null;
// Flag for whether the applet is in a browser
// or running via the main () below.
boolean fInBrowser=true;
//Buttons
JButton fStartButton = null;
JButton fClearButton = null;
JButton fExitButton = null;
// Networking setup
// Properties needed for the connection setup
Socket fServer = null;
DataClientWorker fDataClientWorker = null;
int fDataServerPort
= 2222; // use 2222 as default
String fClientPorfHostt = "";
String fHost =
"127.0.0.1";
String fUserName =
"Smith";
int fChannelToMonitor = 0;
// Amount of data in each set read from the
server
int fNumDataChannels = 10;
// flag for connection status
boolean fConnected = false;
// read data every 500 msecs
int fTimeUpdate = 500;
/**
* Create a User Interface with
a textarea with sroll bars
* and a Go button to
initiate processing and a Clear button
* to clear the textarea.
**/
public void init () {
Container content_pane = getContentPane
();
// Histograms:
// First hist used to show the
values in the data set
// that is obtained in each transfer
from the server.
fHistData = new Histogram ("Data
set values",
"Channel Number",
10,
0.0, 10.0);
fHistDataPanel = new HistPanel
(fHistData);
// Second histogram displays the
distribution of values
// for one of the data channels.
Use an adaptable histogram
// since different channels could
have different data ranges.
fHistChan = new HistogramAdaptR1
("Channel",
"Data Units",
50, 0.0, 50.0,
fHistArraySize);
fHistChanPanel = new HistPanel
(fHistChan);
// The two hists go onto a sub-panel.
JPanel hists_panel = new JPanel
(new GridLayout (2,1));
hists_panel.add (fHistDataPanel);
hists_panel.add (fHistChanPanel);
// Control fields:
// First provide the inputs field
for the host IP
// and for the user name.
fHostField = new JTextField (fHost,16);
JLabel host_label = new JLabel
("Host: ");
host_label.setHorizontalAlignment
(SwingConstants.RIGHT);
fUserNameField =
new JTextField (fUserName,16);
JLabel name_label = new JLabel
("User Name: ");
name_label.setHorizontalAlignment
(SwingConstants.RIGHT);
// Top line of controls = host
and name inputs
JPanel ctrls_panel1 = new JPanel
();
ctrls_panel1.add (host_label);
ctrls_panel1.add (fHostField);
ctrls_panel1.add (name_label);
ctrls_panel1.add (fUserNameField);
// Next line holds the buttons,
and the data
// channel number to monitor.
fStartButton = new JButton ("Start");
fStartButton.addActionListener
(this);
fClearButton = new JButton ("Clear");
fClearButton.addActionListener
(this);
fExitButton = new JButton ("Exit");
if (fInBrowser)
fExitButton.setEnabled
(false);
else
fExitButton.addActionListener
(this);
JPanel buttons_panel = new JPanel
();
buttons_panel.add (fStartButton);
buttons_panel.add (fClearButton);
buttons_panel.add (fExitButton);
JLabel chan_label = new JLabel
("Channel: ");
chan_label.setHorizontalAlignment
(SwingConstants.RIGHT);
fChanField = new JTextField ("0",5);
JPanel chan_panel = new JPanel
();
chan_panel.add (chan_label);
chan_panel.add (fChanField);
fStatusLabel = new JLabel ("Disconnected");
fStatusLabel.setForeground (Color.RED);
fStatusLabel.setHorizontalAlignment
(SwingConstants.CENTER);
// Now pack the components of
the second ctrls
// line of components
JPanel ctrls_panel2 = new JPanel
();
ctrls_panel2.add (buttons_panel);
ctrls_panel2.add (chan_panel);
ctrls_panel2.add (fStatusLabel);
// Put the 2 lines of controls
into a sub-panel
JPanel ctrls_panel12 = new JPanel
();
ctrls_panel12.add (ctrls_panel1);
ctrls_panel12.add (ctrls_panel2);
fMessageArea = new JTextArea ();
fMessageArea.setEditable (false);
// Add to a scroll pane so that
a long list of
// computations can be seen.
JScrollPane area_scroll_pane =
new JScrollPane (fMessageArea);
// Use a GridBagLayout to apportion
space for the
// controls, text area and histograms.
JPanel main_panel = new JPanel
(new GridBagLayout ());
GridBagConstraints c = new GridBagConstraints
();
c.fill = GridBagConstraints.BOTH;
// Put ctrls at top
c.gridx = 0;
c.gridy = 0;
c. weightx = 1.0;
c. weighty = 0.05;
main_panel.add (ctrls_panel12,c);
// Put text area below the controls
c.gridx = 0;
c.gridy = 1;
c. weightx = 1.0;
c. weighty = 0.25;
main_panel.add (area_scroll_pane,
c);
// Put histograms in rest of the
vertical space
c.gridx = 0;
c.gridy = 2;
c. weightx = 1.0;
c. weighty = 0.70;
c.insets = new Insets (2,2,10,2);
main_panel.add (hists_panel, c);
// Add text area with scrolling
to the content_pane.
content_pane.add (main_panel);
} // init
/** Respond to the buttons. **/
public void actionPerformed (ActionEvent e)
{
Object source = e.getSource ();
if (source == fStartButton) {
if (fStartButton.getText
().equals ("Start") )
start
();
else
stop
();
} else if (source ==
fClearButton) {
fHistData.clear
();
// For
adaptable histogram, clear bins
// and
also clear internal data array.
fHistChan.reset
();
repaint
();
} else if (!fInBrowser)// Exit
button
System.exit
(0);
} // actionPerformed
/**
* Make the connection to the server.
Set up the DataReader
* and begin recording the data
from the server.
**/
public void start (){
if (fConnected) stop ();
// Clear the histograms
fHistData.clear ();
fHistData.clear ();
// Get the current values of the
host IP address and
// and the username
fHost = fHostField.getText ();
fUserName = fUserNameField.getText
();
try {
fChannelToMonitor
= Integer.parseInt (fChanField.getText ());
}
catch (NumberFormatException ex) {
println ("Bad channel
value");
return;
}
// Now try to connect to the DataServer
try{
if (connect () ) {
// Successful
so set flags and change button text
fConnected
= true;
fStartButton.setText
("Stop");
fStatusLabel.setText
("Connected");
fStatusLabel.setForeground
(Color.BLUE);
} else {
println
("* NOT CONNECTED *");
fStatusLabel.setText
("Disconnected");
fStatusLabel.setForeground
(Color.RED);
}
}
catch (IOException e) {
println
("* NOT CONNECTED *");
fStatusLabel.setText
("Disconnected");
fStatusLabel.setForeground
(Color.RED);
}
} // start
/**
* Connect to the server
via a socket. Throws IOException
* if socket connection
fails.
**/
boolean connect () throws IOException {
println ("Attempting to connect
to server ...");
try {
// Connect to the
server using the host IP address
// and the port at
the server location
fServer = new Socket
(fHost, fDataServerPort);
} catch (SecurityException se)
{
println ("Security
Exception:\n"+se);
return false;
}
println ("Server connected - create
worker");
// Create the worker to tend to
this server
fDataClientWorker =
new DataClientWorker
(this, fServer, fUserName);
fDataClientWorker.start ();
return true;
} // connect
/** Stop the worker thread. **/
public void stop () {
// Disconnect and kill the fDataClientWorker
thread
fDataClientWorker.finish ();
setDisconnected ();
}
/** Set buttons for restart. **/
void setDisconnected () {
fStartButton.setText ("Start");
fStatusLabel.setText ("Disconnected");
fStatusLabel.setForeground (Color.RED);
}
/**
* The DataClientWorder
passes the data array from the server.
* Display the data
set by packing a histogram.
*
* Also, plot the distribution
of one of the channels of the data.
* The channel number
is given in the text field.
**/
void setData (int [] data) {
// Display each data
set
fHistData.pack (data,
0, 0, 0.0, (double) (data.length) );
fHistDataPanel.getScaling
();
// Plot the distribution
of one of the channels in the data.
if (fChannelToMonitor
>= 0 && fChannelToMonitor < data.length) {
fHistChan.setTitle
("Channel "+ fChannelToMonitor);
fHistChan.add
((double)data[fChannelToMonitor]);
//
Adapt since data varies from channel to channel.
fHistChan.rebin
();
//
Now rescale and draw.
fHistChanPanel.getScaling
();
}
repaint ();
} // setData
/** Convenience method for sending
messages to the text area. **/
public void println (String str) {
fMessageArea.append (str +"\n");
repaint ();
}
/** Create the applet and add to frame. **/
public static void main (String[] args) {
//
int frame_width=500;
int frame_height=650;
// Create standalone version
DataClient applet = new DataClient
();
applet.fInBrowser = false;
applet.init ();
// Following anonymous class used
to close window & exit program
JFrame f = new JFrame ("Data Clent");
f.setDefaultCloseOperation (JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// Add applet to the frame
f.getContentPane ().add ( applet);
f.setSize (new Dimension (frame_width,frame_height));
f.setVisible (true);
} // main
} // class DataClient
|
package DataMonitor;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
/**
* DataClient creates an instance of this thread
class to tend to the
* connectionto the data server.
*
* It periodically requests a set of data from
the server and then
* sends the data to the parent DataClient, which
will update its
* display.
**/
public class DataClientWorker extends Thread
{
// Flag for data running.
boolean fKeepRunning = true;
DataClient fDataClient;
// Networking refs
Socket fServer;
String fUserName;
// I/O with the server
BufferedReader fNetInputReader ;
DataInputStream fNetInputDataStream;
OutputStream fNetOutputDataStream
;
PrintWriter fPrintWriter;
// Number of data values
int fNumChannels = -1;
// Data array
int [] fData = null;
/** Receive the DataClient to provide with the
data from
* the server.
**/
public DataClientWorker (DataClient c, Socket
server, String userName) {
fDataClient = c;
fServer
= server;
fUserName = userName;
}
/** Remain in a loop to monitor the I/O from
the server.
* Display the data.
**/
public void run () {
// The socket connection was made
by the caller, now
// set up the streams and do a login
try {
if (!doConnection
()){
fDataClient.println
(" Connection/login failed");
return;
}
}
catch (IOException ioe) {
fDataClient.println
(" I/O exception with serve:"+ ioe);
}
int num_channels = -1;
// This loops until either the connection
is broken or the
//stop button or stop key is hit
while (fKeepRunning)
{
// Ask the server to
send data.
try {
writeNetOutputLine
(" send data");
}
catch (IOException
e){
break;
}
// First number sent
from server is an integer that gives
// the number of data
values to be sent.
try {
num_channels
= readNetInputInt ();
}
catch (IOException
e) {
break;
}
if (num_channels !=
fNumChannels) {
fNumChannels
= num_channels;
fDataClient.println
(" Number data channels = "
+ fNumChannels);
}
if (fNumChannels < 1){
fDataClient.println
(" no data");
break;
}
// Create an array to
hold the data if not available
if (fData == null ||
fNumChannels != fData.length)
fData
= new int[fNumChannels];
for (int i=0; i < fNumChannels;
i++) {
try {
fData[i]
= readNetInputInt ();
//
Pass the data to the parent program
fDataClient.setData
(fData);
}
catch (IOException
e) {
fDataClient.println
("IO Exception while reading data");
break;
}
}
// Ask for data every
TimeUpdate
try {
Thread.sleep
(fDataClient.fTimeUpdate);
}
catch (InterruptedException
e)
{}
}
if (fServer != null)
closeServer ();
fDataClient.println ("disconnected");
fDataClient.setDisconnected ();
} // run
/** Set up the streams with the server and then
login. **/
boolean doConnection () throws IOException {
// Get the input and output streams
from the socket
InputStream in = fServer.getInputStream
();
// Use the reader for obtaining
text
fNetInputReader = new BufferedReader
(
new InputStreamReader
(in)) ;
// User the DataInputStream for
getting numerical values.
fNetInputDataStream = new DataInputStream
( in );
// Output stream for sending messages
to the server.
fNetOutputDataStream = fServer.getOutputStream
();
// Write with a PrintWriter for
sending text to the server.
fPrintWriter= new PrintWriter (
new OutputStreamWriter
(fNetOutputDataStream, "8859_1"), true );
// Now try the login procedure.
if (!login ()) return false;
return true;
} // doConnection
/** Here is a homemade login protocol. A password
could
* easily be added.
**/
boolean login () {
fDataClient.println ("Waiting for
login prompt...");
String msg_line=readNetInputLine
();
if (msg_line == null) return false;
fDataClient.println (msg_line);
if (!msg_line.startsWith ("Username:"))
return false;
fDataClient.println ("Send username
" + fUserName);
try {
writeNetOutputLine (fUserName);
}
catch IOException e) {
return false;
}
catch (Exception e) {
fDataClient.println
("Error occurred in sending username!");
return false;
}
fDataClient.println ("Waiting for
response...");
msg_line=readNetInputLine ();
if (msg_line == null) return false;
fDataClient.println (msg_line);
return true;
} // login
/** Do all of the steps needed to stop the connection.
**/
public void finish (){
// Kill the thread and stop the
server
fKeepRunning = false;
closeServer ();
}
/** Close the socket to the server. **/
void closeServer () {
if (fServer == null) return;
try {
fServer.close ();
fServer = null;
}
catch (IOException e)
{}
}
/**
* The net input stream is wrappped in
a DataInputStream
* so we can use readLine, readInt and
readFloat
**/
String readNetInputLine () {
try {
return fNetInputReader.readLine
();
}
catch (IOException e) {
return null;
}
}
/** Read an integer value from the socket stream
**/
int readNetInputInt () throws IOException {
return fNetInputDataStream.readInt
();
}
/** Read float value from the socket
stream. **/
float readNetInputFloat () throws IOException
{
return fNetInputDataStream.readFloat
();
}
/**
* The net output is a PrintWriter
class which doesn't throw
* IOException itself. Instead we
have to use the PrintWriter
* checkError () method and throw
an exception ourselves if there
* was an output error.
**/
void writeNetOutputLine (String string) throws
IOException {
fPrintWriter.println (string);
if (fPrintWriter.checkError ())
throw (new IOException ());
fPrintWriter.flush ();
if (fPrintWriter.checkError ())
throw (new IOException ());
} // writeNetOutputLine
} // class DataClientWorker
|
Last update: Dec. 11, 2004
|
|
|

