| Home : Course Map : Chapter 15 : |
|
The Client/Server Data Monitor: Step by Step
|
| JavaTech |
| Course Map |
| Chapter 15 |
|
Client/ServerDesign |
| About
JavaTech Codes List Exercises Feedback References Resources Tips Topic Index Course Guide What's New |
|
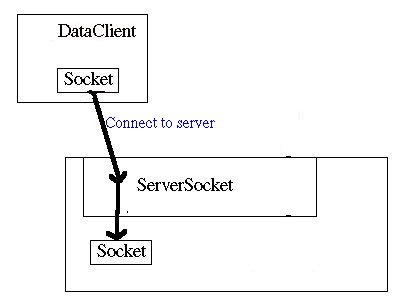
We show here the essential steps involved in our data client/server system: We start the DataServer and it sits patiently waiting for clients to arrive. The client starts on another machine (or on the same machine for convenience during testing ) and connects to the server using the socket type connection discussed in Chapter 14:
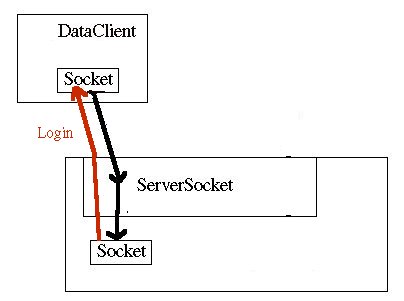
A simple log-in in procedure occurs in which the server requests that the client send a username. The client responds with a arbitrary name string. You could easily expand this capability to include both a username and password:
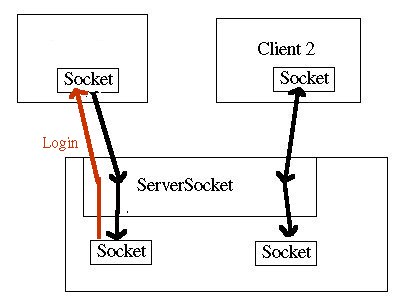
Diagram 2: Client & server execute a login procedure.. Another client could also simultaneously request a connection to the server with the same procedure:
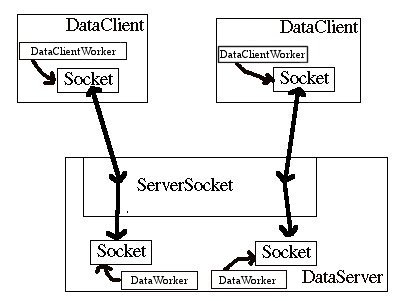
Diagram 3: Another client connects to the server. The server assigns an instance of the Thread subclass called DataWorker whose job is to communicate with a particular client over the socket and to perform the requested tasks. Similarly, the client creates an instance ofof the Thread subclass DataClientWorker to carry out communications with the server.
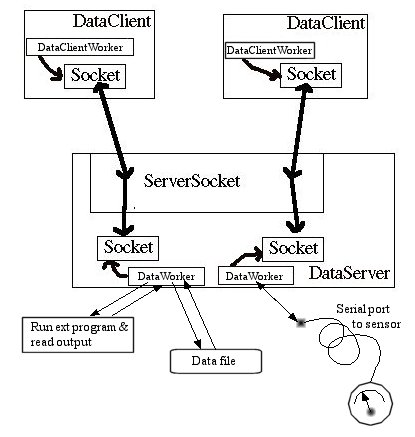
For an application, the DataWorker might grab data from a file and send it to the DataClient where the DataClientWorker can process it:
Figure 15.5 illustrates other data taking scenarios such as reading data from an instrument over a serial or parallel port. It could also run an external program and read its output. In Chapter 23 we will discuss how Java programs can reach out to the external world outside of the JVM. Latest update: Dec. 10, 2004
|