| Home : Course Map : Chapter 14 : |
|
Security Manager & Policy Files
|
| JavaTech |
| Course Map |
| Chapter 14 |
| About
JavaTech Codes List Exercises Feedback References Resources Tips Topic Index Course Guide What's New |
|
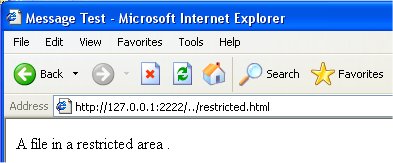
Our MicroServer program has a serious flaw. As shown below, it potentially makes available for viewing almost any file on the platform. For example, a user might put have the browser use a URL like this: http://www.myHost.com:2222/../restricted.html where the ".." will refer to the directory above the directory where the server code is located. To illustrate this we create a file with the code:
and place it in the directory above our server code location. Then our browser reads this file from our server without difficulty:
To control access to resources in Java programs, a system involving the SecurityManager class, policy files, permissions, and other tools are available. Security is a big issue in Java so we can only touch here on a few aspects of it. In the following sections we show the basics of how to make our server program more secure. To restrict a Java program's access to system resources, you can load a SecurityManager object that controls access to such resources. An instance of the SecurityManager class must be installed when an application first begins. If not, then the default null manager puts the server into a completely unprotected state. (For applets running in a browser JVM, the security manager severely restricts the actions allowed.) Before Java 1.2 you needed to create a subclass of SecurityManager to customized your security requirements. The SecurityManager class holds many methods of the form checkXXX(args), such as checkDelete(String file), that throw an instance of SecurityException to block the particular action XXX. Your subclass must override those methods for the actions that you want to allow or to block only for particular circumstances. For example, in the case of deleting a file, your overriding version of checkDelete(String file) method could examine the file name and path to determine if you want to allow its deletion. This approach to security, however, requires hardcoding and is very clumsy considering the large number of different types of system access operations now available to Java programs. With Java 1.2 a much more fexible permissions based security system was introduced. In this approach, a security policy file, in text format, is checked by the security manager for granted actions. (What isn't granted is forbidden.) For example, if the policy file - myRules.policy - contains the entry
then it would allow the application to delete those files in the directory C:\Java\apps\ that end with the ".tmp" suffix but no others. We will discuss more about the details of policy file and permissions in the More Security section. The application installs the security manager from the command line, rather than in the program, and specifies the policy file using the "-D" option as in: c:> java -Djava.security.manager -Djava.security.policy=myRules.policy MyApp This approach to configuring the security for access to the system provides for much greater flexibility and clarity than customizing a SecurityManager subclass that must be recompiled after every modification.. We use our server to illustrate how to set up security permissions for file access. In MicroServer there is no protection against the client requesting any file on the system. To control access to where the application can reach files, we use the policy file microServer.policy in which we put:
The server must access a socket and since this is an external resource, a permission statment is required. So we permit the program to listen for, accept, and connect with any socket via port 1024 and up by using the symbol "1024-". Similarly, for the file permission case we indicate with "/-" that the program can access files in the server directory and any subdirectories but not above this directory. We put this policy into the directory c:\Java\MicroServer\Secure\ (note that the grant statement must use forward slashes regardless of the platform) where we also put the server code. To catch the instances of SecurityException that can now be thrown, we create a new version of the thread class Worker that is identical the previous version except that it adds a catch statement in the run() method as shown below:
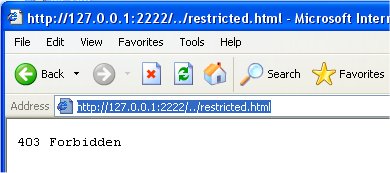
We rename the program to MicroServerSecure, though it's code is identical to the MicroServer class, simply to indicate that we are working with the new version of Worker. We run this server with the following command line: java -Djava.security.manager -Djava.security.policy=microServer.policy MicroServerSecure (which should be on one continuous line). The client browser shows the following when we attempt to download the restricted file:
The security exception was thrown when the attempt to access restricted.html was made. It then sent the "403 Forbidden" message. References & Web Resources
Latest update: Jan. 9, 2004 |